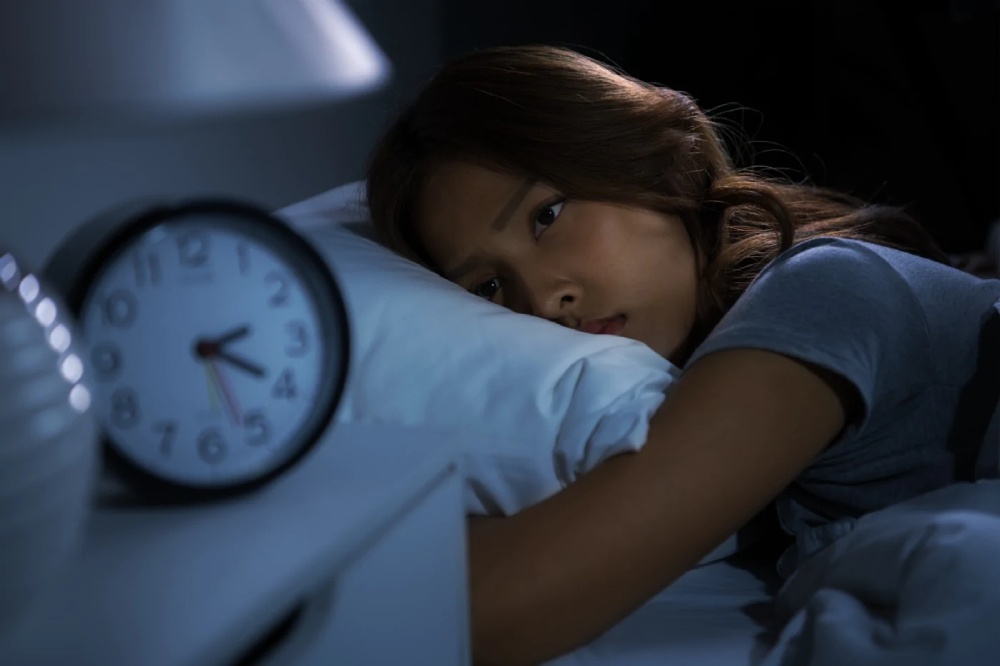
Insomnia may be related to many things. You might have trouble sleeping due to a relationship, money, work, or any other matter. About one-third of individuals have some insomnia at any one time. Stress isn’t usually the cause of these sleep problems, but it may worsen them when it is.
It is a common observation that a lack of sleep might make you feel slower intellectually and more emotional, which can heighten your sense of stress. And if the reason for insomnia is stress, then being exhausted won’t help deal with the issues that are causing the stress. Persistent insomnia may lead to stress, which might result in more insomnia. Stress-related insomnia is a constant cycle of tension and sleeplessness.
Stress and Anxiety
Anxiety and stress are concerns as they can affect many other activities. Anyone can suffer from these issues. However, if you experience them often, it may be an anxiety problem. It may lead to severe episodes that increase your blood pressure, pulse rate, and perspiration. Ultimately it will also affect sleep and may lead to insomnia.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a medical condition that affects sleep patterns and creates problems in staying and falling asleep. Chronic insomnia is what you experience if it occurs at least three times a week for more than three months. Insomnia may increase your risk of developing other medical issues, such as an anxiety disorder.
Types of Insomnia
According to a medical perspective, various approaches assess each severe type of insomnia.
Insomnia severity can be divided into five categories, highlighted in a 2019 study published in The Lancet Psychiatry. Most of the people surveyed in the study did not alter their responses during that time. Because of this, it is thought that many types of insomnia can remain largely consistent for a person’s lifetime.
There are five types of insomnia:
- Acute insomnia
- Chronic insomnia
- Comorbid insomnia
- Onset insomnia
- Maintenance insomnia
What Is the Link Between Anxiety and Insomnia?
Stress and anxiety throughout the day often continue into the evening, leading to insomnia. It can lead to “mental hyperarousal.”
An anxiety disorder can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep long enough to relax your mind and body. Anxiety functions as your body’s alarm system, helping to keep you safe and out of potentially hazardous circumstances. However, if that alarm constantly sounds without apparent cause, as it does in cases of anxiety disorders, it may prevent you from enjoying adequate deep sleep.
Stress-related difficulty falling asleep or getting adequate sleep might result from all of this. And it could make you feel even more anxious.
Additionally, there is an indication that a persistent lack of sleep might impact your mental well-being. According to research, obstructive sleep apnea, which causes frequent waking, increases the risk of mental health problems, including anxiety, panic disorder, and depression.
Effect of Stress on Sleep
The body’s internal clock system, which informs the body when it is time to sleep and when it is time to stay alert, is affected because of chronic stress. Individuals are more likely to have difficulty falling asleep and report poor sleep patterns when they are under stress throughout the day. Deep sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which are both crucial for both physical and mental health, may be affected by stress. Dream patterns and emotional content can also be affected by stress.
The sleep-wake cycle is significantly impacted by the amount of the stress hormone cortisol. Researchers have shown that patients with insomnia have higher levels of cortisol in the evening, which are connected in turn to a larger number of nocturnal awakenings; cortisol typically drops at night to prepare for sleep. Additional study is required to determine whether sleep disorders raise cortisol levels or whether high cortisol levels induce insomnia.
Some scientists believe that a stressful incident might lead to short-term sleeplessness; they have described this response as a normal reaction to possible danger. It may be difficult to fall asleep due to the acute physiological changes brought on by fight-or-flight responses, listed below.
Muscle Tension:
Muscle tension is one of the characteristics of a stress reaction. The body’s main muscle groups tighten up in preparation for future damage or discomfort. However, excessive stress might prevent the kind of relaxation required for restful sleep.
Elevated Heart Rate:
Stress-related symptoms include fast breathing and an accelerated heart rate: Restful sleep must have a slower heartbeat and breathing.
Digestive System Effects:
An upset stomach, diarrhea, or constipation are common effects of high stress on the digestive system that may be painful while attempting to go asleep.
Treatment of Insomnia
Initially, doctors manage sleeping issues like insomnia by altering sleeping patterns and taking care of any problems that may be contributing to the insomnia like anxiety, stress, underlying medical disorders, or drugs. If these steps are unsuccessful, your doctor may advise cognitive behavioral therapy, medication, or a combination of the two to aid sleep and relaxation.
Prescription Medications
Doctors prescribe these medicines to assist you in getting to sleep and staying asleep. However, it is also interesting to note that they are not prescribed for more than a few weeks. On the other hand, several prescription medicines are prescribed for long-term use.
- Alprazolam
- Bromazepam
- Eszopiclone
- Ramelteon
- Zaleplon
- Zolpidem
However, prescription drugs for insomnia have several side effects, including
- Physical and psychological dependence
- Day-time drowsiness
- Increasing the risk of falling
So you must report these side effects to your doctor if you are using prescription medicines for insomnia.
Over-the-counter sleep aids
Over-the-counter antihistamines may cause drowsiness, but they’re not meant to be taken regularly. You must consult your doctor, since antihistamine side effects may be severe in older persons. They include daytime drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, cognitive impairment, and issues related to urinating.